Understanding Heat Pumps: The Efficient Heating Solution
Published on May 4, 2024
Ever wondered how you can efficiently heat large volumes of water or air for your industrial processes without burning traditional fuels? The answer might be simpler and greener than you think: Heat Pumps.
What Exactly is a Heat Pump?
Think of a heat pump like a refrigerator working in reverse. Instead of removing heat from an enclosed space (like your fridge) and releasing it outside, a heat pump extracts available heat from a source – like the ambient air, water, or ground – and transfers it to where it's needed, such as heating water for industrial processes or warming a space.
It's not creating heat; it's moving it. This fundamental difference is why heat pumps are incredibly energy-efficient.
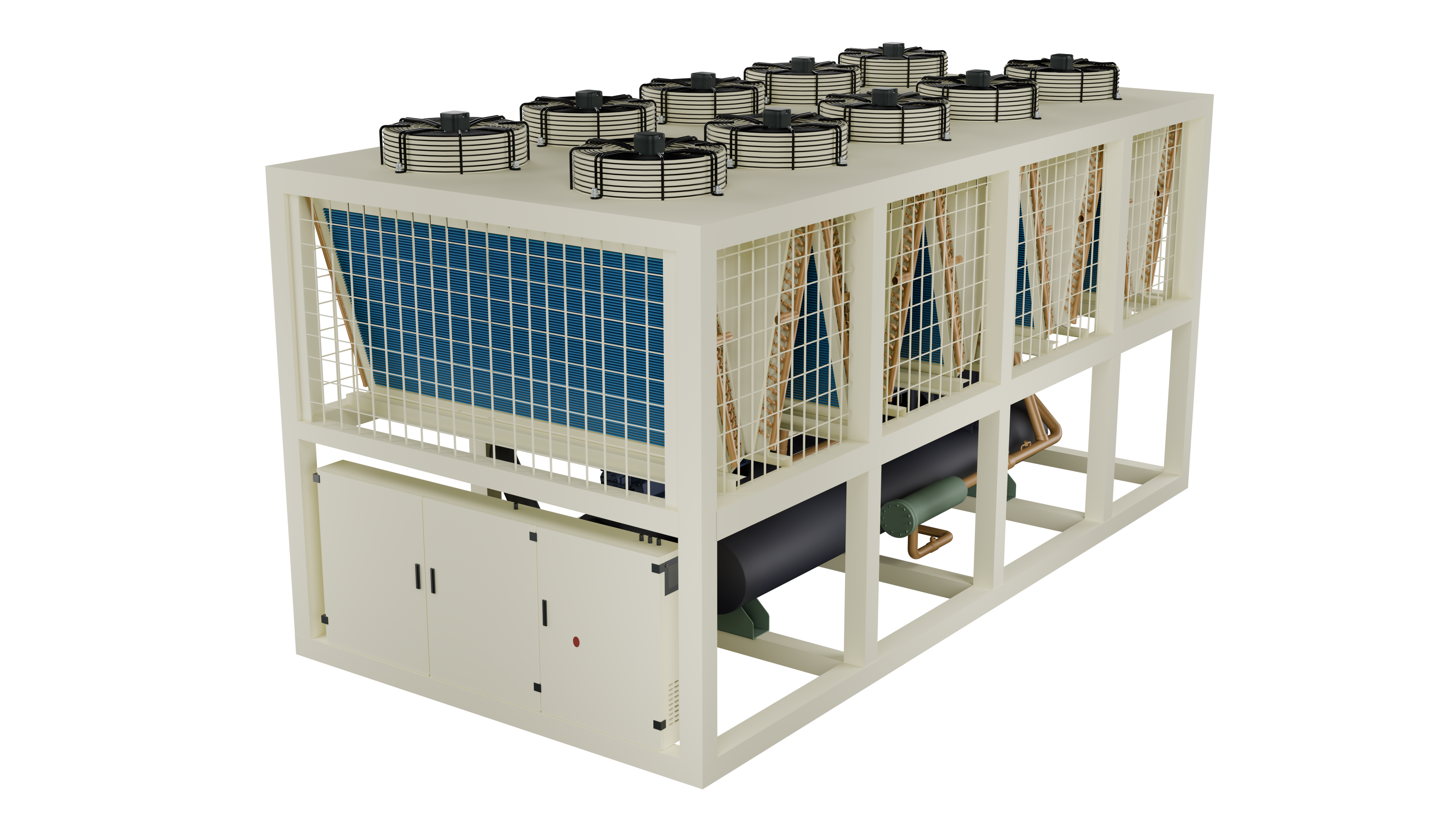
How Does It Work? The Operational Principle
The magic behind a heat pump lies in the refrigeration cycle. It uses a refrigerant, a special fluid that evaporates and condenses at specific temperatures and pressures. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Evaporation: The cold, liquid refrigerant flows through an outdoor coil (the evaporator). It absorbs heat from the surrounding air, water, or ground, causing the refrigerant to boil and turn into a gas.
- Compression: This low-pressure gas is then passed through a compressor. Compressing the gas significantly increases its temperature and pressure.
- Condensation: The hot, high-pressure gas moves to an indoor coil (the condenser). Here, it releases its heat to the target medium (e.g., water or air). As it cools down, the refrigerant condenses back into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion: The high-pressure liquid passes through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature, returning it to its initial cold liquid state, ready to start the cycle again.

Why Are Heat Pumps Gaining Popularity Now?
Several factors are driving the increased adoption of heat pumps in industrial settings:
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps can achieve Coefficients of Performance (COP) of 3 to 5 or even higher. This means for every unit of electrical energy consumed by the compressor, they deliver 3 to 5 units of heat energy. This drastically reduces energy consumption compared to traditional boilers or electric heaters.
- Lower Operating Costs: Reduced energy consumption directly translates to significant savings on energy bills.
- Environmental Benefits: By primarily moving heat rather than generating it through combustion, heat pumps produce far fewer greenhouse gas emissions, especially when powered by renewable electricity sources. This helps companies meet sustainability goals and regulations.
- Versatility: Industrial heat pumps can be designed for various applications, from process water heating and drying to space heating, often utilizing waste heat streams as a source, further boosting efficiency.
- Government Incentives: Many regions offer subsidies or tax credits for installing energy-efficient technologies like heat pumps.
Is a Heat Pump Right for Your Operation?
Heat pumps offer a compelling combination of efficiency, cost savings, and environmental responsibility. If you're looking to optimize your heating processes, reduce your carbon footprint, and lower operational expenses, exploring heat pump technology is a smart move.
Ready to Learn More?
Discover how Titan Heat Pump solutions can be tailored to your specific industrial needs.
Contact Us Today